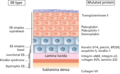
Figure 71.1
Epidermis and basement membrane illustrating the different levels where blisters occur in subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa (EB) as well as the locati...
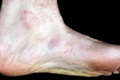
Figure 71.5
Autosomal recessive acral peeling skin syndrome resembling autosomal dominant localized epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
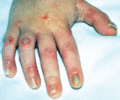
Figure 71.9
Acral blisters and nail dystrophy in a patient with epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy due to autosomal recessive mutations in plec...
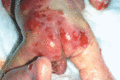
Figure 71.13
Extensive erosions over the buttocks in an infant with severe generalized junctional epidermolysis bullosa.
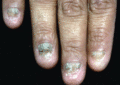
Figure 71.17
Nail dystrophy in generalized intermediate junctional epidermolysis bullosa.
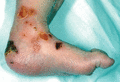
Figure 71.21
Acral blistering in (dominant) bullous dermolysis of the newborn in a 2‐month‐old male infant. By the age of 9 months the blistering had ceased and on...
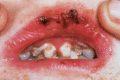
Figure 71.25
Dental caries and blistering on the lips in severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St J...
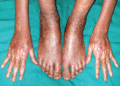
Figure 71.29
Poikiloderma in a 12‐year‐old Indian patient with Kindler syndrome.
Figure 71.33
Electron microscopy of part of a basal keratinocyte in severe generalized epidermolysis bullosa simplex showing tonofilament clumping (TF) and cytolys...
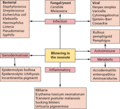
Figure 71.37
Differential diagnosis of skin blistering in a neonate.
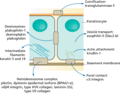
Figure 71.2
The collection of proteins involved in the pathogenesis of epidermolysis bullosa.
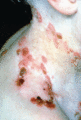
Figure 71.6
Grouped blisters on an erythematous base in generalized severe epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
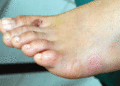
Figure 71.10
Localized blistering on the foot in a patient with autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex due to autosomal recessive mutations in BP230. (...
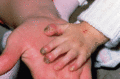
Figure 71.14
Nail changes in severe generalized junctional epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St John's Institute of Dermatology, London...
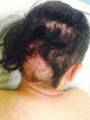
Figure 71.18
Scalp alopecia and hair thinning in generalized intermediate junctional epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor E. Sprecher, Tel Aviv, Israel.)...
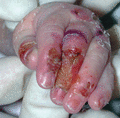
Figure 71.22
Blisters and erosions on the hand in a 4‐week‐old child with severe generalized recsssive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
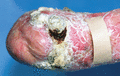
Figure 71.26
Squamous cell carcinoma on the scarred hand of a 35‐year‐old patient with severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
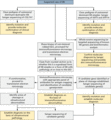
Figure 71.30
Outline of the laboratory approach to diagnosing epidermolysis bullosa (EB). DEJ, dermal–epidermal junction.
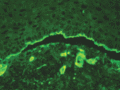
Figure 71.34
Antigen mapping of type IV collagen to a blister roof in a patient with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (sublamina densa blistering).
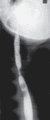
Figure 71.38
Barium swallow radiograph showing constriction in the upper oesophagus in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J....
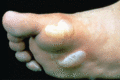
Figure 71.3
Blisters on the foot in a patient with localized epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
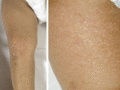
Figure 71.7
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation on the lower limb in an 18‐month‐old child. (Courtesy of Dr J. E. Mellerio, St John's Institu...
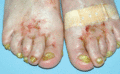
Figure 71.11
Erosions on the feet and nail dystrophy in ectodermal dysplasia‐skin fragility syndrome (acantholytic EB simplex – plakophilin‐1).
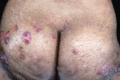
Figure 71.15
Erosions, scarring and atrophy on the buttocks in a patient wth generalized intermediate junctional epidermolysis bullosa.
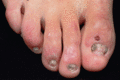
Figure 71.19
Nail changes and scarring of skin on the toes in dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St John's Institute...
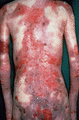
Figure 71.23
Extensive lesions on the back in severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St John's Insti...
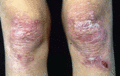
Figure 71.27
Scarring on the knees in a 14‐year‐old patient with generalized intermediate recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
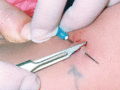
Figure 71.31
Shave biopsy technique suitable for the investigation of suspected epidermolysis bullosa.
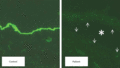
Figure 71.35
Immunolabelling for type VII collagen in normal skin showing bright linear staining at the dermal–epidermal junction. In contrast, in a patient with s...
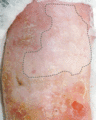
Figure 71.39
Revertant mosaicism in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Spontaneous correction of a COL7A1 mutation has occurred in the skin within the d...
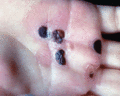
Figure 71.4
Blisters, some of which are haemorrhagic, and erosions on the palm in a patient with localized epidermolysis bullosa simplex.
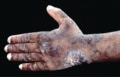
Figure 71.8
Acral blistering in a patient with autosomal recessive epidermolysis bullosa simplex with loss of keratin 14 expression in the skin.
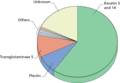
Figure 71.12
Molecular basis of EB simplex. The majority of mutation are in keratins 5 and 14, transglutaminase 5 and plectin. The small group of ‘other’ proteins ...
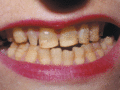
Figure 71.16
Pitting and discoloration of teeth in generalized intermediate junctional epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St John's Inst...
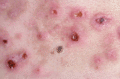
Figure 71.20
Inflammatory skin blistering in epidermolysis bullosa (EB) pruriginosa (dystrophic EB) resembling an acquired immunobullous disease.
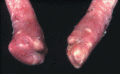
Figure 71.24
Mitten hand deformity in severe generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J. Eady, St John's Institute of ...
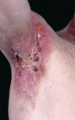
Figure 71.28
Scarring and erosions affecting the axilla and neck in the inversa form of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. (Courtesy of Professor R. A. J...
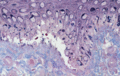
Figure 71.32
Intraepidermal cleavage revealed by light microscopy (semi‐thin section) in severe generalized epidermolysis bullosa simplex (Huber stain).
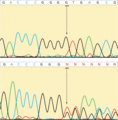
Figure 71.36
Sanger sequencing. The upper image shows a wild‐type DNA sequence but in the lower image there is a 1 bp deletion (G nucleotide) that induces a frames...

