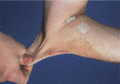
Figure 72.1
Cutaneous hyperextensibililty in classical Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.
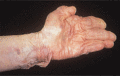
Figure 72.5
Extreme cutaneous fragility and laxity in dermatosparaxis.
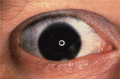
Figure 72.9
Blue sclera in osteogenesis imperfecta.
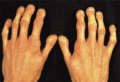
Figure 72.13
Familial mandibuloacral dysplasia, showing the short club‐shaped terminal phalanges, the so‐called ‘tree‐frog’ appearance. (Courtesy of Dr A. M. Zina...
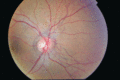
Figure 72.17
Right fundus showing angioid streaks radiating from the optic nerve in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. (Courtesy of Miss Louise Allen, Cambridge University...

Figure 72.2
Atrophic scarring of the elbow in classical Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.
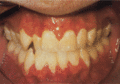
Figure 72.6
Premature periodontal recession in periodontitis type Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (type VIII).
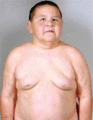
Figure 72.10
Autosomal dominant cutis laxa in a 13‐year‐old male. (Reproduced from Berk et al . 2012 [ ]. Reproduced with kind permission of Elsevier.)
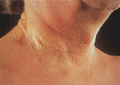
Figure 72.14
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum, showing the typical ‘chicken skin’ appearance involving the neck.
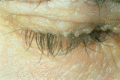
Figure 72.18
Lipoid proteinosis. Typical ‘beaded’ papules present along the margins of the upper eyelids. (Courtesy of Dr R. C. D. Staughton, Chelsea and Westmins...

Figure 72.3
Scarring of the forehead in classical Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.
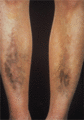
Figure 72.7
Pigmented pretibial plaques in periodontitis type Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (type VIII).
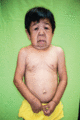
Figure 72.11
Autosomal recessive type IA cutis laxa due to FBLN5 mutation in a 4‐year‐old girl. Generalized loose skin affecting the trunk, limbs and most eviden...
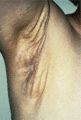
Figure 72.15
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum of the axilla, showing the characteristic yellow discoloration of the skin and the loose folds. The changes in this condition...

Figure 72.4
Cutaneous atrophy in vascular (acrogeric) Ehlers–Danlos syndrome.
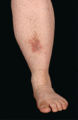
Figure 72.8
Pitted skin in prolidase deficiency. (Courtesy of Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, UK.)

Figure 72.12
Child with Williams–Beuren syndrome exhibiting later facial features of full cheeks and lips, periorbital puffiness and epicanthic folds. (Copyright o...
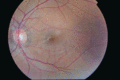
Figure 72.16
Left fundus showing angioid streaks at the macula which have caused deterioration of the central vision. A mottled appearance ‘peau d'orange’ can be s...

