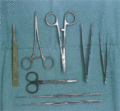
Figure 03.1
Instruments for skin biopsy, including scalpel, scissors, needle holder and skin hooks.

Figure 03.5
(a) Connective tissue naevus. The section stained with H&E only shows focal condensation of the collagen. (b) An elastic van Gieson stain shows marked...
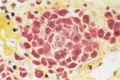
Figure 03.9
Chloroacetate esterase stain. Mast cells appear red with this technique.
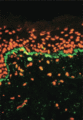
Figure 03.13
Direct immunofluorescence of lupus erythematosus showing speckled basement membrane zone deposition of IgM (green) and ethidium bromide counterstain (...
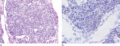
Figure 03.17
(a) Typical example of a Merkel cell carcinoma consisting of hyperchromatic cells with scanty cytoplasm. (b) Immunostaining with cytokeratin 20 highli...

Figure 03.21
(a) Subacute spongiotic process (eczema) with hyperplasia of Langerhans cells presenting in a large nest within the epidermis mimicking a Pautrier mic...

Figure 03.25
Bizarre multinucleated giant cells from a Spitz naevus.
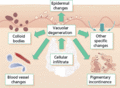
Figure 03.29
Lichenoid tissue reaction. Various histopathological consequences follow damage to the dermal–epidermal junction. These histopathological changes are ...
Figure 03.2
Disposable punch for cutaneous biopsy.
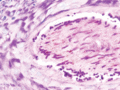
Figure 03.6
Periodic acid–Schiff stain showing numerous hyphae within the hair shaft in an endothrix infection.
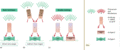
Figure 03.10
Different immunofluorescence techniques: (a) direct, (b) indirect and (c) double staining.
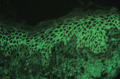
Figure 03.14
Direct immunofluorescence of pemphigus showing deposition of intercellular IgG in the epidermis.

Figure 03.18
(a) Extramammary Paget disease showing prominent colonization of the epidermis by numerous, atypical, rounded cells with pink cytoplasm. (b) Tumour ce...
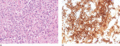
Figure 03.22
(a) Sheets of large, atypical lymphoid cells with pleomorphic nuclei and pink cytoplasm. (b) Positive staining of atypical cells in a case of CD30‐pos...
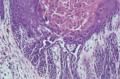
Figure 03.26
Biopsy from a case of Darier disease showing the histological features of parakeratosis, dyskeratosis and acantholysis and the formation of villi.
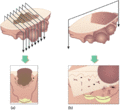
Figure 03.3
Blocking of elliptical skin biopsy specimens. (a) Neoplastic lesions. Multiple transverse blocks through the whole lesion allow for histopathological ...
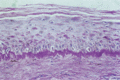
Figure 03.7
Periodic acid–Schiff stain showing thickening of the basement membrane zone in cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
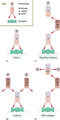
Figure 03.11
Different immunoperoxidase techniques: (a) direct, (b) indirect, (c) modified indirect and (d) with peroxidase–antiperoxidase (PAP) complex.
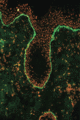
Figure 03.15
Direct immunofluorescence of bullous pemphigoid showing linear basement membrane zone deposition of IgG (green) and ethidium bromide counterstain (ora...
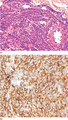
Figure 03.19
(a) Glomus tumour composed of uniform, round cells with pale cytoplasm and well‐defined cytoplasmic membrane. (b) Strong cytoplasmic staining for smoo...
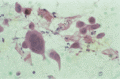
Figure 03.23
An H&E‐stained smear from a lesion of herpes simplex showing multinucleate giant cells and degenerative nuclear changes.
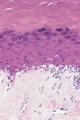
Figure 03.27
Prominent liquefaction degeneration from a case of lichen sclerosus.

Figure 03.4
Photocopy procedure for recording the preparation of blocks. (a) The appearance of a macroscopic specimen of melanoma. (b) Transverse blocks are taken...

Figure 03.8
(a) A prominent lymphocytic infiltrate which is focally lichenoid and is associated with extravasation of red blood cells in a case of lichen aureus (...
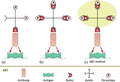
Figure 03.12
Avidin–biotin staining methods. (a) Antibody coupled with biotin binds with the antigen in the tissue. Avidin coupled with peroxidase binds to the bio...

Figure 03.16
(a) Poorly differentiated tumour composed of pleomorphic spindle‐shaped cells in the dermis (H&E). (b) Diffuse positivity of tumour cells for the pan‐...

Figure 03.20
(a) Typical dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans composed of monotonous, spindle‐shaped cells with hyperchromatic nuclei arranged in a prominent storiform ...
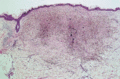
Figure 03.24
Extensive dermal pigmentation as a result of the application of Monsel's solution.

Figure 03.28
Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis seen in a biopsy from a patient with congenital bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma.

